The National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR) has completed the rebasing of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), updating the reference year from 2017 to 2024 to better reflect changes in the economy.
Rebasing, an exercise carried out every three years, had been delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, making this Rwanda’s first update in seven years.
Announcing the results, officials explained that rebasing captures structural changes in the economy, such as new industries, shifts in agriculture, tourism developments, and changes in construction and land values. “This exercise ensures that our GDP figures provide a more accurate picture of the economy’s current structure and value,” NISR said.
The rebased figures show that Rwanda’s GDP for 2024 rose to US$19,918 billion, a 6% increase from the previously published US$18,785 billion.
However, this revision also adjusted the growth rate for 2024 downward from 8.9% to 7.2%.
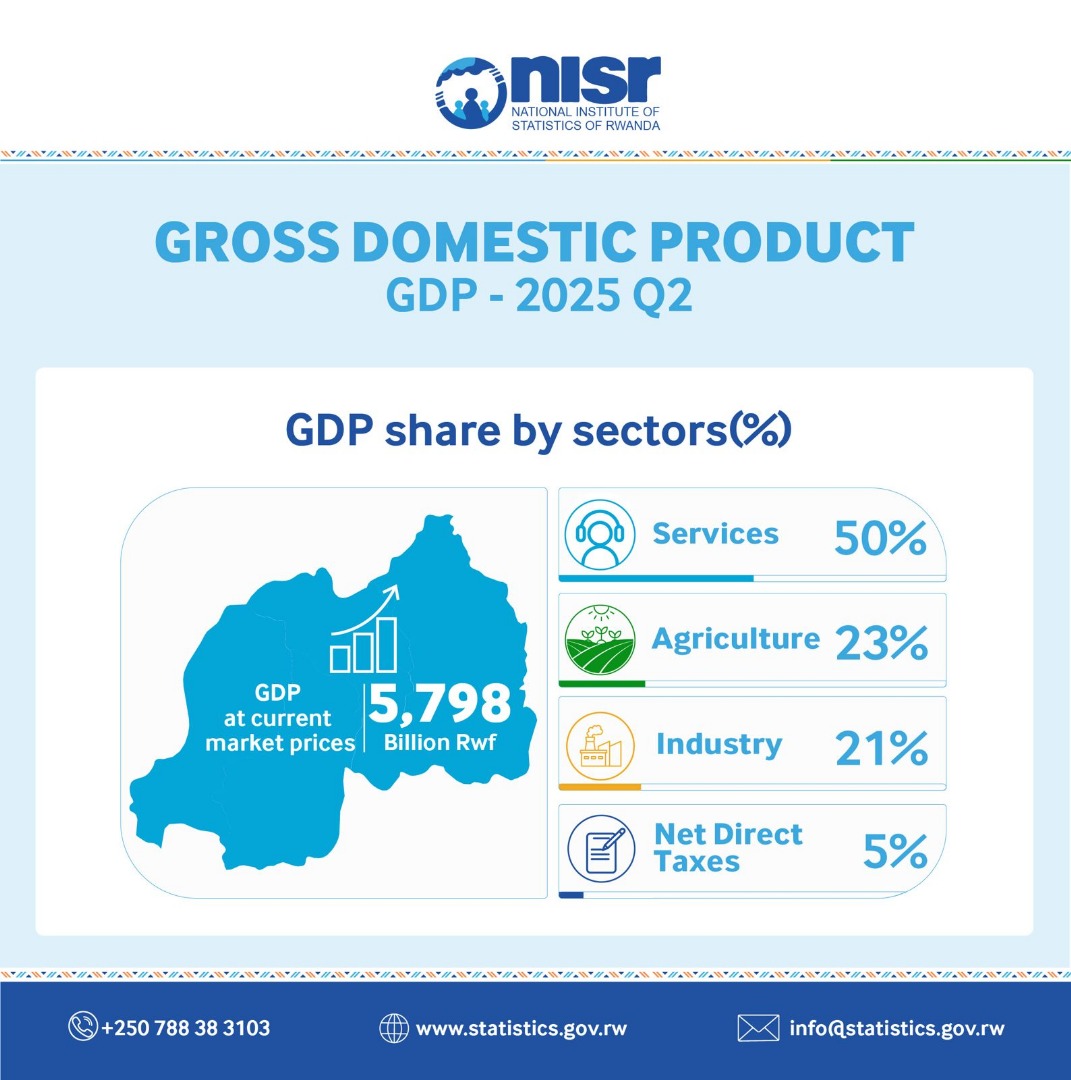
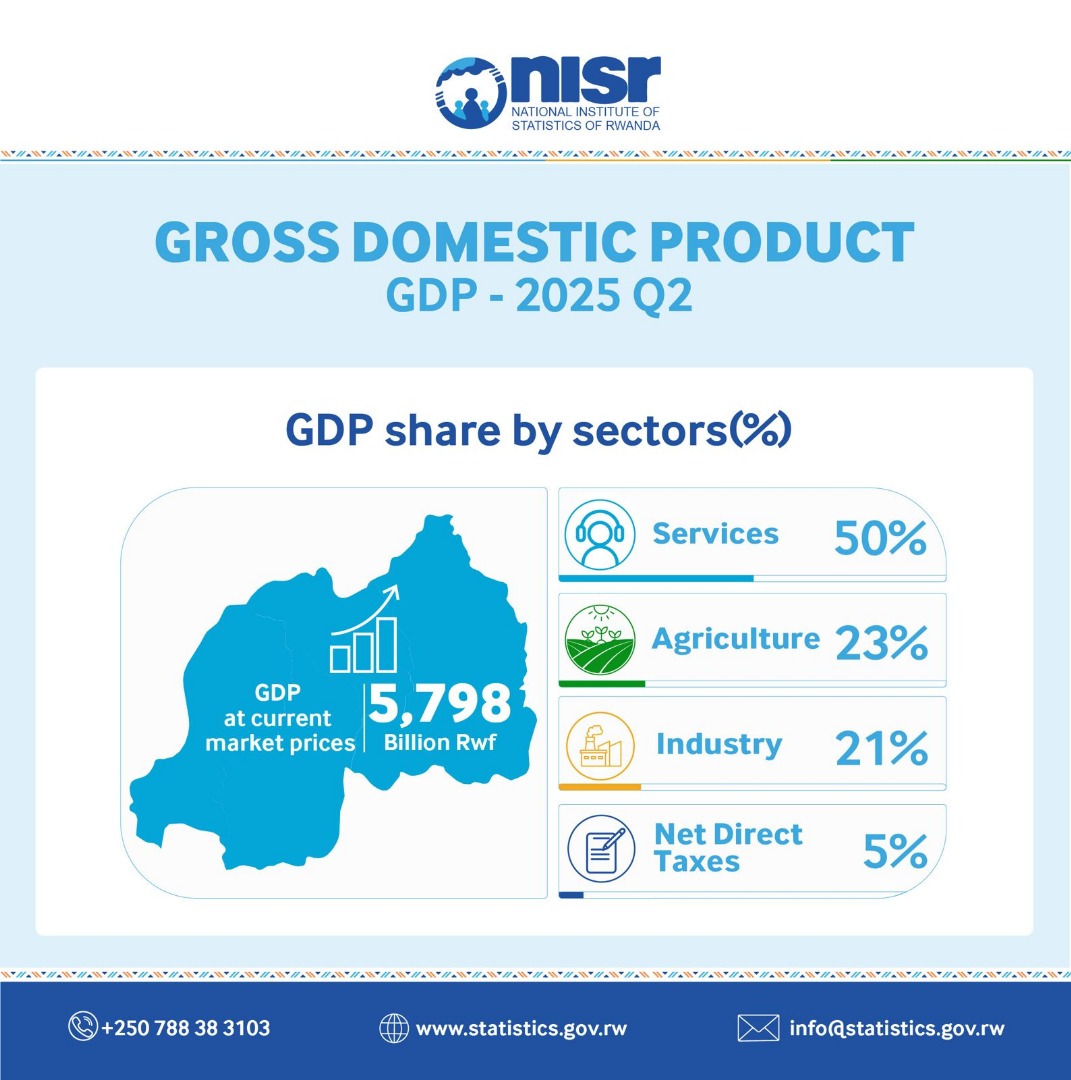
For Q2 2025, GDP at current market prices was estimated at US$5,798 billion, marking a 7.8% increase compared to 6.5% in Q1. Services contributed the largest share of GDP at 50%, followed by agriculture at 23% and industry at 21%.
Agriculture grew by 8%, boosted by a 10% rise in food crop production and a 42% surge in export crops, driven largely by improved coffee yields.
Tea production, however, dropped by 9%. Industry grew by 7%, led by a 12% increase in mining and quarrying, an 8% rise in manufacturing, and a 5% expansion in construction.
Services posted 9% growth, with wholesale and retail trade up 12%, financial services up 8%, restaurants and transport up 5%, and information and communication recording an 11% jump.
All figures presented are based on the new reference year of 2024, which NISR says aligns with international best practices recommending GDP rebasing every five to ten years.